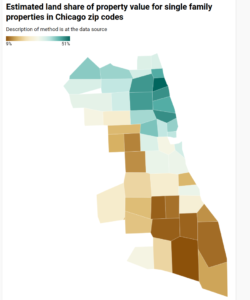
UPDATE Aug 29 2021: If anyone familiar with Chicago doubts that removing improvements from the tax base will ease the burden on low-income homeowners, this map will be instructive. The original, mapless post from Aug 25 follows.
We sometimes are told that a land value tax (LVT) would punish the poor person who has a small rundown house on a high-value lot, while benefiting the person next door who has a large fancy house on an identical lot. And that’s not wrong, it’s just atypical. In practice, we believe, poor people mostly live in neighborhoods where housing is cheap and land is cheaper, thus they would tend to benefit from a shift to LVT.
As the quality of Cook County assessments has been improving, we expect to be able to show this by analysis of that data. In the meantime, we have some estimates of land and improvement value from William Larson and colleagues at the Federal Housing Finance Agency. Using appraisals produced for mortgage underwriting, they estimate land and improvement values for homes in most zip codes (and census tracts) nationwide. Their source data includes only single family properties which were appraised for mortgage purposes. They consider only parcels where the improvement is less than 15 years old, and exclude vacant land as well as land where the appraised value is very close to the assessed value (in case appraisers might have relied on low-quality or obsolete assessments). Also excluded are zip codes with an insufficient number of single family home transactions.
The chart below shows, for Chicago zip codes, the ratio of land value to total value (vertical axis) and total value of the property (horizontal axis. What stands out is that the ratio tends to be lower where the properties are cheaper. That is, a revenue-neutral shift of property taxation to land values only, ignoring value of improvements, would tend to reduce the taxes on low-value zip codes, while increasing it in higher-value areas.
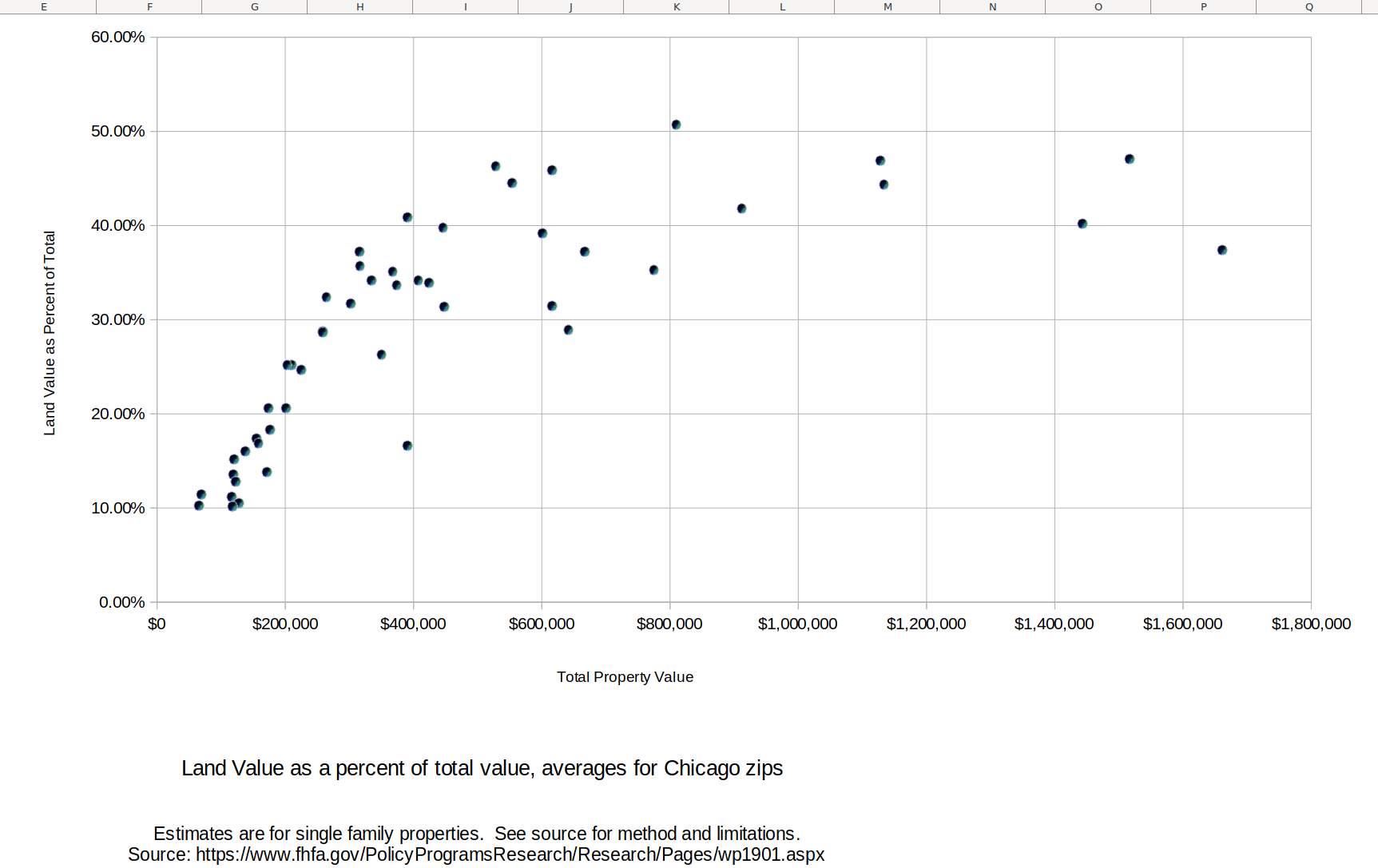
The table below shows the data for each zip code, sorted from high proportion of value in land to low. Clearly the more affluent areas have lower proportion of improvement value, and the areas with low income population have a higher proportion of improvement value.
| Estimated land value proportion and related data for single family properties in Chicago zip codes | |||||
| ZIP Code | Lot Size | building sq ft | floor area ratio | Property Value (As-is) | Land Share of Property Value |
| 60640 | 4300 | 2320 | 0.540 | $809,500 | 50.70% |
| 60614 | 2920 | 2950 | 1.010 | $1,516,300 | 47.10% |
| 60613 | 3740 | 2590 | 0.693 | $1,128,200 | 46.90% |
| 60625 | 4220 | 1860 | 0.441 | $528,000 | 46.30% |
| 60618 | 3580 | 1890 | 0.528 | $615,800 | 45.90% |
| 60660 | 3820 | 1940 | 0.508 | $553,500 | 44.50% |
| 60657 | 3210 | 2600 | 0.810 | $1,133,300 | 44.40% |
| 60622 | 3120 | 2330 | 0.747 | $911,800 | 41.80% |
| 60631 | 5620 | 1690 | 0.301 | $390,700 | 40.90% |
| 60610 | 2250 | 2900 | 1.289 | $1,443,300 | 40.20% |
| 60646 | 5370 | 1820 | 0.339 | $445,900 | 39.80% |
| 60647 | 3250 | 1880 | 0.578 | $600,800 | 39.20% |
| 60654 | 1990 | 3580 | 1.799 | $1,661,200 | 37.40% |
| 60630 | 4310 | 1550 | 0.360 | $315,500 | 37.20% |
| 60642 | 2230 | 2140 | 0.960 | $667,200 | 37.20% |
| 60641 | 4230 | 1640 | 0.388 | $316,400 | 35.70% |
| 60605 | 1840 | 2200 | 1.196 | $774,700 | 35.30% |
| 60659 | 4310 | 1800 | 0.418 | $367,500 | 35.10% |
| 60626 | 5410 | 2050 | 0.379 | $407,400 | 34.20% |
| 60656 | 5100 | 1500 | 0.294 | $334,600 | 34.20% |
| 60612 | 2910 | 1920 | 0.660 | $424,300 | 33.90% |
| 60645 | 4420 | 1870 | 0.423 | $373,600 | 33.70% |
| 60634 | 4240 | 1470 | 0.347 | $264,100 | 32.40% |
| 60608 | 2960 | 1530 | 0.517 | $302,200 | 31.70% |
| 60615 | 4460 | 2630 | 0.590 | $615,700 | 31.50% |
| 60616 | 2570 | 1950 | 0.759 | $447,900 | 31.40% |
| 60607 | 1970 | 2140 | 1.086 | $641,400 | 28.90% |
| 60655 | 5140 | 1490 | 0.290 | $258,000 | 28.80% |
| 60707 | 4940 | 1600 | 0.324 | $258,700 | 28.70% |
| 60637 | 3920 | 1970 | 0.503 | $350,000 | 26.30% |
| 60609 | 3320 | 1450 | 0.437 | $209,700 | 25.20% |
| 60639 | 3900 | 1420 | 0.364 | $202,900 | 25.20% |
| 60638 | 4280 | 1340 | 0.313 | $225,100 | 24.70% |
| 60632 | 3860 | 1300 | 0.337 | $173,600 | 20.60% |
| 60643 | 5960 | 1600 | 0.268 | $200,800 | 20.60% |
| 60652 | 4730 | 1330 | 0.281 | $176,400 | 18.30% |
| 60629 | 4040 | 1340 | 0.332 | $155,300 | 17.40% |
| 60651 | 3920 | 1440 | 0.367 | $158,300 | 16.90% |
| 60653 | 3290 | 2360 | 0.717 | $390,100 | 16.60% |
| 60644 | 4580 | 1650 | 0.360 | $137,400 | 16.00% |
| 60633 | 4690 | 1320 | 0.281 | $120,200 | 15.20% |
| 60649 | 4960 | 1870 | 0.377 | $170,800 | 13.80% |
| 60623 | 3510 | 1340 | 0.382 | $118,500 | 13.60% |
| 60624 | 3300 | 1540 | 0.467 | $122,200 | 12.80% |
| 60621 | 3880 | 1490 | 0.384 | $69,300 | 11.50% |
| 60617 | 4200 | 1360 | 0.324 | $116,300 | 11.20% |
| 60619 | 4320 | 1430 | 0.331 | $127,700 | 10.50% |
| 60636 | 3540 | 1270 | 0.359 | $65,200 | 10.30% |
| 60620 | 4180 | 1410 | 0.337 | $117,800 | 10.20% |
| 60628 | 4320 | 1340 | 0.310 | $99,800 | 9.20% |
| source: | https://www.fhfa.gov/PolicyProgramsResearch/Research/Pages/wp1901.aspx | ||||
A Chicago zip code map is here.
Also of interest, even tho the low-value areas have a high ratio of improvement to land value, this isn’t because of large houses on small lots. The floor area ratio is generally lower in the areas with lower land value proportion.
Overall, the above data is consistent with Georgists’ assertion that low-income residents usually benefit from a switch to LVT. I might be taking a further look at this dataset.